Last Updated on 11/09/2020 by Veronica Jones

Rabies in dogs and cats is an acute infectious disease that is common to many warm-blooded animals and humans. It is caused by a neurotransmitter. The virus affects the brain so the animal has neurological symptoms such as madness, confusion, polio and death.
Epidemiology
Rabies was known and described as early as 2300 BC in Ancient Egypt and Greece. In 1804, the infectiousness of dog saliva was discovered. In 1882, the infectiousness of saliva from herbivore and humans with rabies was known.
By injecting saliva into rabbits, Pasteur and his students discovered that the brains of infected animals contain a lot of the virus. And, they have successfully developed the rabies vaccine, opening a new era in rabies prevention in livestock. The first patient (7/1885) who was saved after being bitten by a rabid dog was Joseph Meister. After, 350 people were subsequently saved with the vaccine (only one girl who was bitten by a rabid dog died after 1-month treatment).
Rabies is caused by an RNA virus called Lyssavirus, belong to the Rhabdoviridae group. The rabies viruses collected from natural samples are called “street rabies” (street virus).
- The street rabies virus can cause disease in humans and animals. If this virus is injected many times to rabbits, when injecting to humans and other animals, they will not get rabies but create immunity. It is called the fixed virus.
- The rabies virus develops in the nerve cells of almost all warm-blooded and some cold-blooded animals.
- In outer conditions, the rabies virus is a resistant strain of the virus. At 56oC, the virus is killed after 30 minutes, at 70oC, the virus dies immediately.
- Antiseptic such as formol 1%, cresol 3% and beta-propiolactone 0.1% can disable the virus.
- The virus can exist in the brain of rabies animals for 10 days at room temperature, for several weeks at 4oC and 3-4 years at negative temperatures.
- Phenol 0.5%, which can preserve the virus in the brain of rabies, allows the sample to be sent for testing without refrigeration.
- In nature, all warm-blooded animals are most infected, especially dogs and cats. Animals can be infected at any age.
- In the rabies animals, the virus is found in many nervous organs such as the brain, spinal cord or salivary glands.
- In the salivary glands, the virus is present 3 – 17 days before the animal becomes clinically ill.
- Eyes, corneas, urine, liver, spleen, adrenal glands, lungs contain viruses.
-
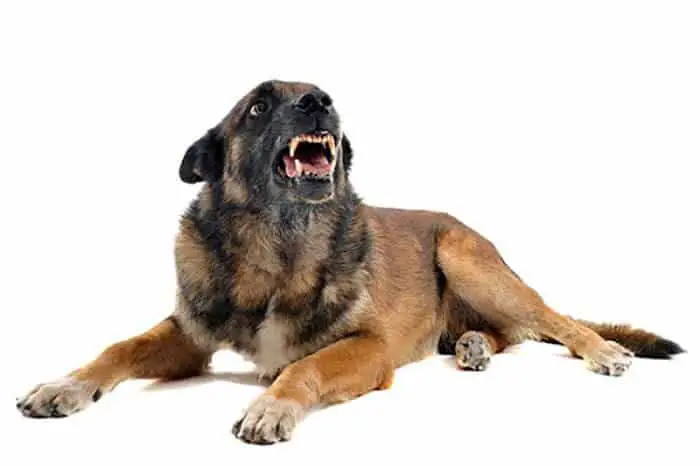
Rabies Virus Cause Disease in Dogs and Cats
-
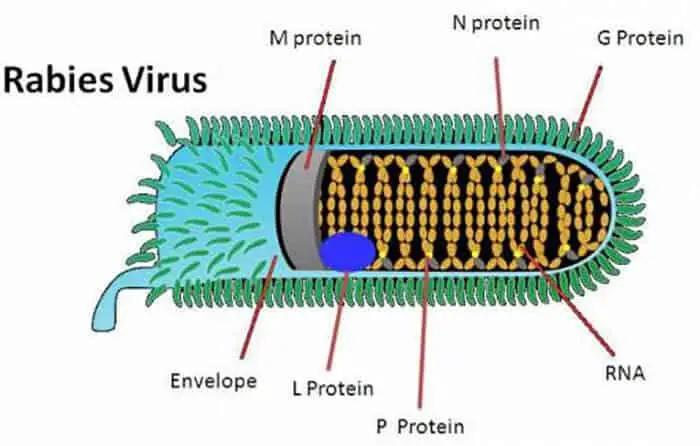
Rabies Virus belongs to RNA Group
Read more >>> Scabies in Dogs: [A-Z] Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment,…
Mode of transmission
In the majority of cases, the animal appears rabies symptoms disease after being bitten by animals that are infected with rabies. In a few cases, it is caused by the virus entering mucosa or open wounds.
In some cases, rabies occurs through inhalation of the virus in the air in bat burrows or by mucosal contact.
Animals bitten by other animals infected with rabies are 30-40% more likely to be infected. The cause can be explained as follows:
- The onset of the disease depends on the bite. If the bite is deep, wide, the possibility of rabies is higher.
- If the wound is bleeding, it can be considered a self-cleaning process and pushing the virus out of the way: the possibility of rabies is reduced.
- The person or object that is bitten has a cover (human clothing, thick hair in sheep …) will absorb saliva, reducing the amount of virus entering the wound.
- If being bitten by a rabies dog, immediately cleaning and applying an antiseptic, it will reduce the chance of getting sick.
- In some cases, when the virus enters the body, it will remain in the body for a long time before the symptoms appear. This explains there is a record of a person who was bitten by a rabid dog had rabies symptoms after 7 years.
-
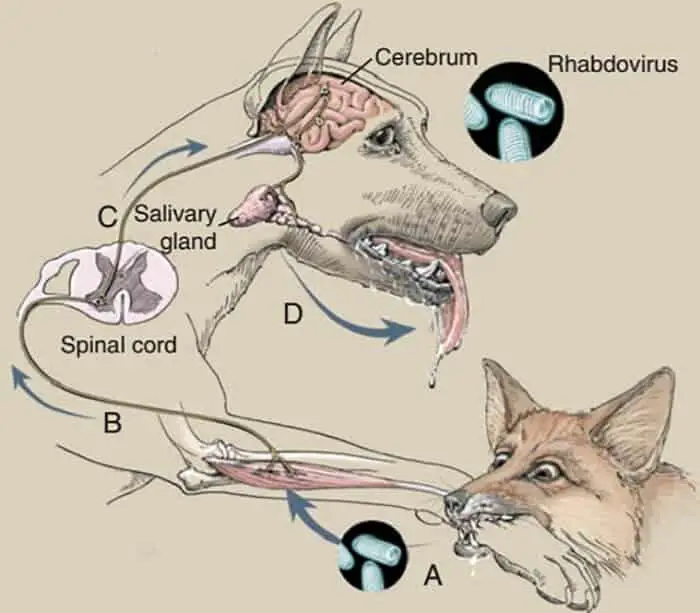
Method of transmission of rabies in dogs
Mechanism of pathogenesis
When entering the body, the virus is neurotropic, so it will penetrate the peripheral nerves and move to the central nervous system. The speed of movement of the virus in the nerve is 0.5 – 1mm / hour.
- In the brain, the virus follows the nerve move to the organs.
- In the first stage, the number of viruses is limited, so it affects only a small number of neurons, animals do not show rabies symptoms.
- In the later stage, the virus multiplies, they destroy the nerve cells. The animal appears with neurological symptoms such as madness, confusion, tearing, psychological disorder.
- After that, the neurons will be severely damaged, the animal is paralyzed and then dies. In most cases, animals die from respiratory paralysis.
Read more >>> Calcium Deficiency Seizure in Dogs and Cats ( Before and after giving childbirth)
Symptoms of rabies
- Rabies in dogs has a very variable incubation period from 14 to 90 days. But it can last longer from 2 to 7 years after being bitten by a rabies animal.
- The incubation time depends on the location of the bite, the depth of the bite, the amount of virus invaded, outer conditions … The closer the bite is to the brain and spinal cord, the shorter the incubation time is.
- The incubation time of young animals is higher than that of adults.
Symptoms of the dog with rabies
There are two forms of Rabies: encephalitic and paralytic.
Encephalitis
Account for approximately 15 to 20% of dogs with rabies (70% in tropical countries). Clinical rabies expression is divided into 3 periods:
Opening period
- Dogs have many strange expressions such as a change in personality, sad expressions.
- Occasionally barking idly or biting air (fly-catching), fidgeting.
Stimulate period
- Suddenly standing up, jumping.
- Dogs react excessively to sound or light.
- The pupils of the eye are wide open, easily startled.
- Stop eating, thirsty, drink water continuously but only drink very little.
- Saliva flows as much as “soap bubbles”.
- After 2-3 days: the dog’s eyes are bloodshot, the ears are upside down, the mouth is open, the lower jaw comes down, the drool is flowing, the belly is sagging.
- If the dog is not to be locked out, they will run away.
- During an attack, the dog bit around objects until it broke its teeth without making a sound. The rabies is often interspersed with depression, the dog sits quietly, his face dazed with fear.
Polio period
The animal is paralyzed by muscles, cannot eat and swallow. The saliva drips out a lot, the lower jaw comes down completely. They can die from exhaustion due to the movement of rabies and not eating or drinking.
-
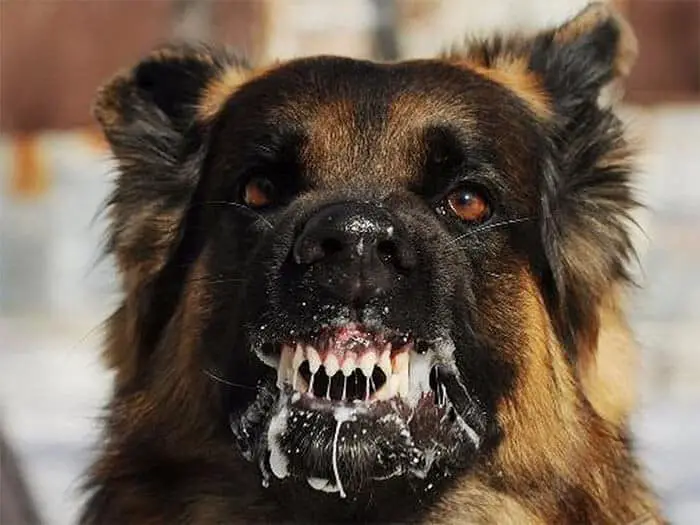

Symptoms of Rabid Dog in Encephalitic Form
Paralytic:
- The animal shows no signs of fury, and other symptoms are similar to an encephalitic form.
- Puppies usually have rabies in this form.
- After a rabies attack, most animals get sick lasting 5-7 days, sometimes limited only 2 days or some even last up to 14 days.
- In some cases, infected dogs can be cured (5 – 6%), the virus remains in the dog’s body for a long time.
-

Symptoms of Rabid Dog in Paralytic Form
Rabies in cats
- Cats are less prone to rabies than dogs.
- An infected cat will appear sad, find a private place to lie down, or cry out, irritated. After that, the disease quickly turns into paralysis and dies.
- The disease in cats is very dangerous because cats are very close to people. And when a cat biting, the wounds are deep.
-
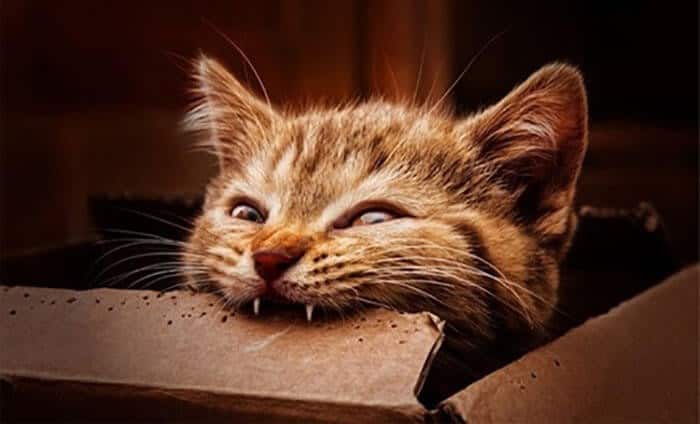

Rabid Wild Cat
Rabies in cattle
Cattle with rabies become seriously angry, stand unsteady, glare, saliva flowed, hit anything or people nearly, then turn into paralysis and die.
- Rabies in cattle is mainly transmitted by rabies in a dog.
Lesions
General injury
Characteristics of animals such as:
- The stomach does not contain anything or contains an undigested object such as straw, a piece of wood, a piece of bone, a stone …
- The lining of the stomach and the small intestine become bleeding.
- Hemorrhage, cerebral congestion.
Microscopic lesions
- Negri was found in the brain, especially in the Hippocampus.
-
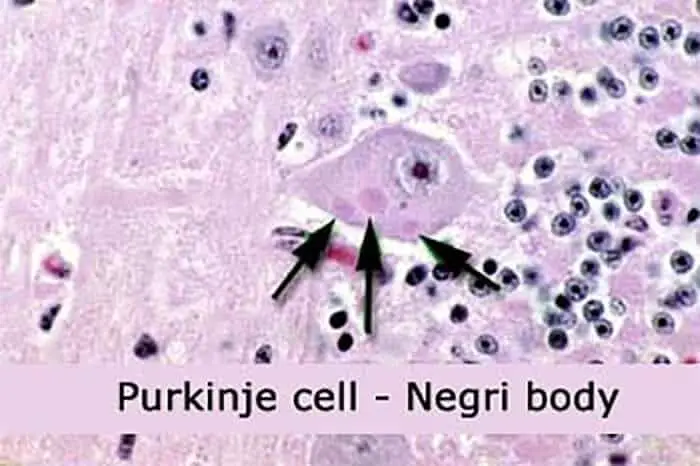
Negri Bodies that Cause Rabies in Dogs and Cats
Diagnose
Clinical diagnosis
- Due to the dangerous nature of rabies to humans, objective science demands precision. There should be a concept of a dog with suspected rabies without a precise claim for rabies.
- When a dog is suspected of being rabid, treat it like a rabid dog.
- It is allowed to falsely predicate that an animal has rabies, but it is not allowed to incorrectly confirm that an animal does not have rabies.
Routine diagnostic methods
There are 3 basic methods of diagnosis and must be carried out simultaneously:
- Find the Negri
- Fluorescence diagnosis
- Diagnosed by virus culture method
Results from the 3 methods complement each other. If only one result is positive, the animal is considered having rabies.
Sample: brain, salivary glands of animals suspected of being infected.
Other diagnostic methods
Currently, it is possible to use highly accurate laboratory diagnostic methods such as ELISA, RT-PCR, neutral reaction. Field diagnosis with POCKIT iiPCR technique for fast results within 1-2 hours.
Read more >>> Symptoms and Diagnosis of Care Disease in Dogs ( Febris Catarrhalis Infectiosa Canum)
Rabies prevention
Measures for the whole pack of dogs
- Eliminate the links related to each other during the onset of the disease.
- Register to raise a dog, punish the dog owner.
- Inject rabies vaccine in dogs.
- Destroy animals which are suspected of having rabies, confine, or kill a dog without an owner.
- Wear muzzle, chain when walking dogs.
Prevention with vaccine
- Annual inject rabies vaccine to prevent diseases for livestock.
-

Annual inject vaccine to prevent rabies in dogs and cats
How to treat people when bitten by a dog
- When being bitten by a dog, immediately wash the wound with soap and antiseptics (eg 70% alcohol and 5% iodine).
- Immediately go to the medical facility, the center for preventive health services to get advice from a doctor and inject antisera and vaccines.
- When vaccinating dogs for rabies it is important to keep in mind:
- The vaccine may cause slight local reactions such as redness, itching, etc., but these reactions will go away after a few days.
- Those who have a predisposition to allergies, chronic illnesses, or alcohol addiction may experience a slight fever, headache, nausea, and dizziness after injection (usually after the 3rd injection onwards).
- However, the proportion of people with these side effects is very low. When the above symptoms are present, the patient must notify the doctor at the clinic for timely action.
Treatment of rabies in dogs and cats
Pets which is suspected of having rabies are not allowed to be treated at home. The owner must immediately notify the local veterinary agency for action. Do not arbitrarily sell or treat animals with suspected rabies.
Rabies in dogs and cats is very dangerous, develops quickly, causing many tragic deaths for pets. Vetguru always accompanies with farmers in the diagnosis of rabies with many modern, advanced technology equipment at reasonable prices.
Immediately contact at hotline 0983.600.953 for direct advice from experts.


