Last Updated on 11/09/2020 by Veronica Jones

Scabies in Dogs is contagious diseases caused by a parasite, also known as scabies. They attack the epidermis, burrowing into the nest, causing the infected host to itch and uncomfortable so that it can become infected.
What types of scabies are most common in dogs
1. Sarcoptes Scabies
The most common type of scabies in dogs is caused by the parasite named Sarcoptes Scabiei Canis. They dislocate under the epidermis to collect the tricuspid fluids, the cellular fluid that nourishes the body and secretes enzymes proteases that weaken the horny stratum for easier mobility. The life cycle of this species is from 15 to 20 days.
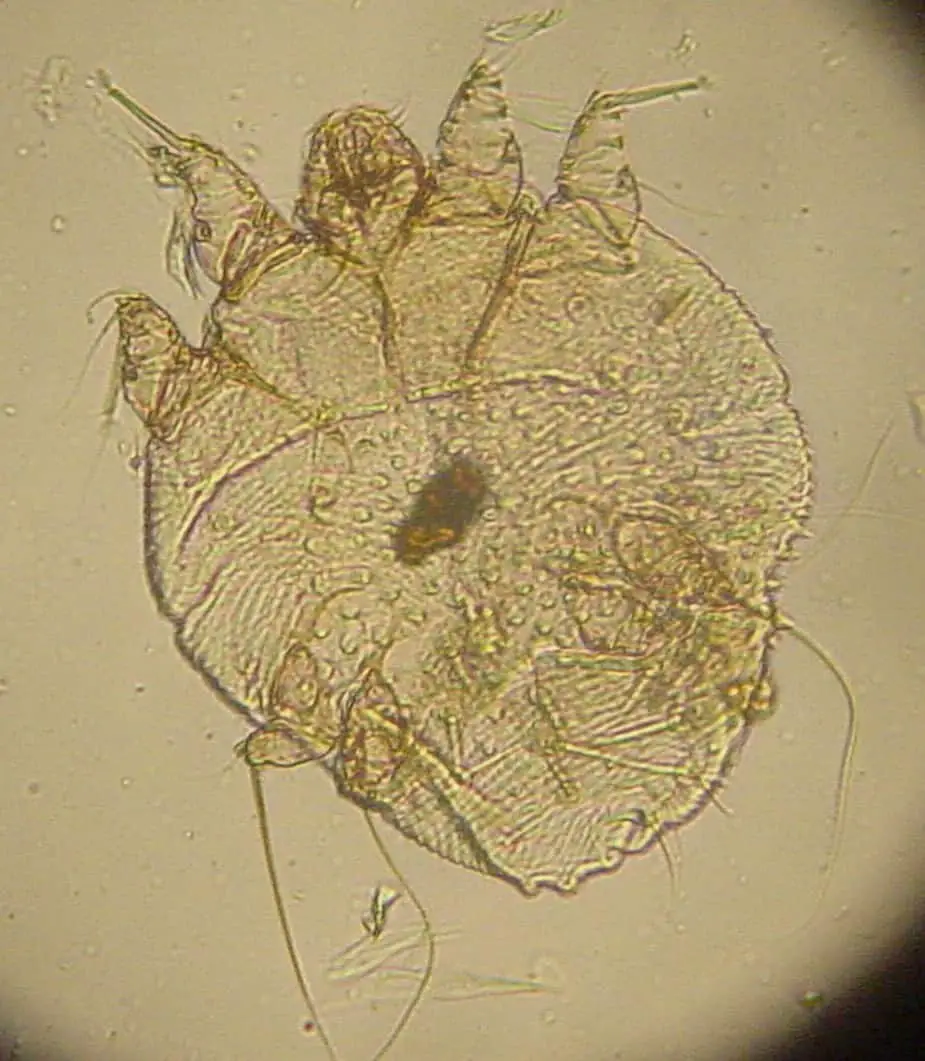
The parasite Sarcoptes scabiei Canis
– Sarcoptes scabies does not pose much danger to dogs but is easy to transmit to humans, especially children.
– Symptoms:
- Sarcoptes usually parasitize around the abdomen, armpit, groin, ear base, around the breast. On the surface of the skin, there is an inflammatory exudate and after it dries it will become a scaly layer containing pus.
- Dog start itching and discomfort then scratching with feet, gnawing with teeth causes pustules to burst. In severe cases, the dog’s body appears the symptoms of flaking and shedding due to secondary infection by fungi and bacteria.
- Dogs lose their appetite, stop eating, and sleeping because of itching, which causes rapid weight loss.
2. Demodex Scabies
– Caused by the Demodex Canis parasite. With a special body structure, the pointed shape helps them easily dig deep into the skin to nest, parasitize in hair follicles and sebaceous glands, absorb nutrients, and sebum from the coat.
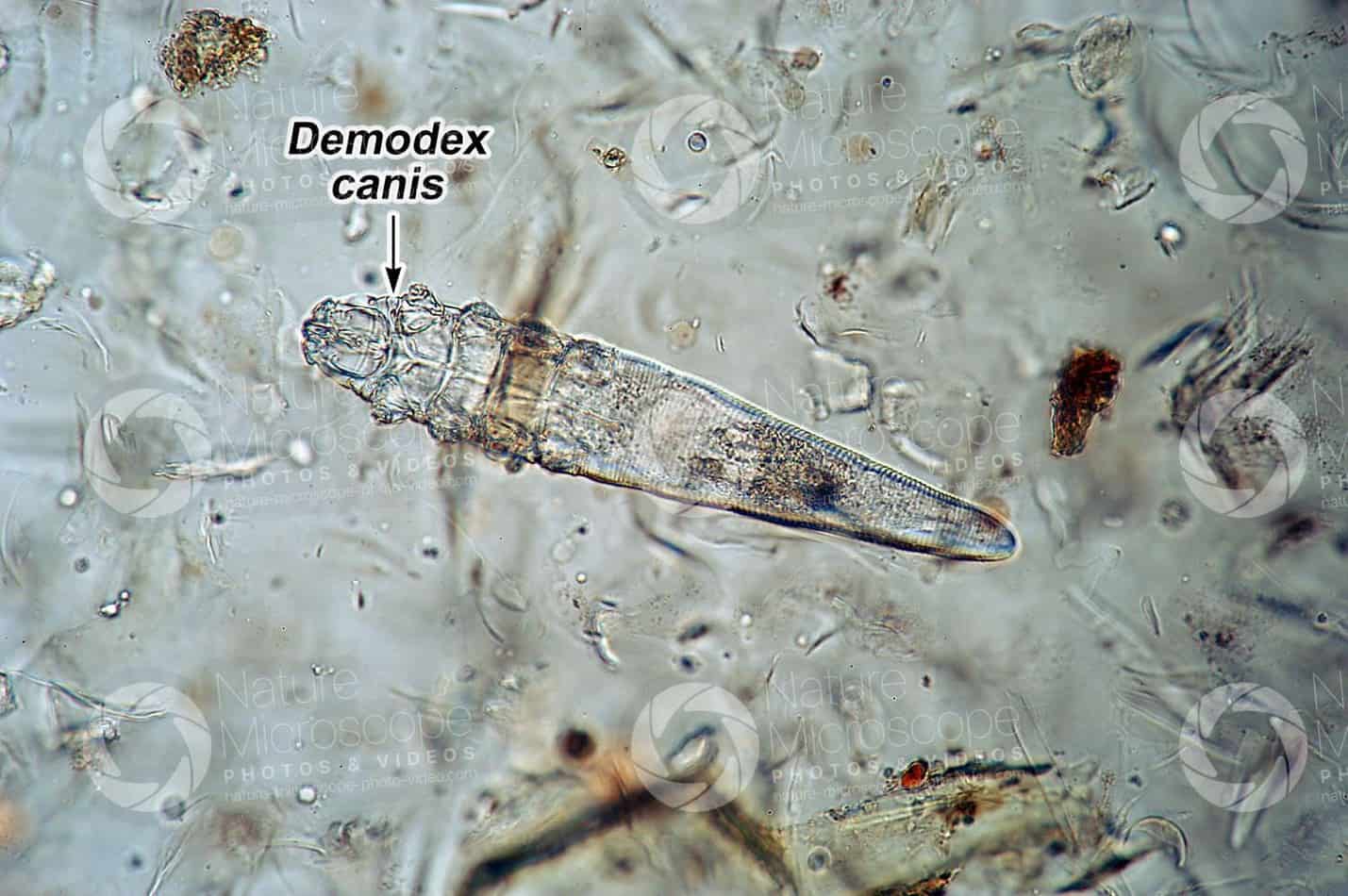

- The parasite Demodex Canis
– This type of scabies is hard to rescue, Demodex life cycle is 20-35 days.
– Symptoms:
- The dog’s coat falls out gradually, unevenly, forming different thin-thick hair patches. Usually, this small patch of skin will not become severely inflamed, itchy, or irritated but go away on its own.
- About 90% of dogs with local scabies can go away on their own after 1-2 months, but if worse, dogs with itchy, can bite themselves, turn the condition into large-scale scabies (usually due to genetics from parents).
Diseased dogs have a bad smell, wrinkled skin, inflamed, pus, and blood plasma discharge does not coagulate.
This type of scabies can not be spread to humans as well as rarely transmit to the same species.
-
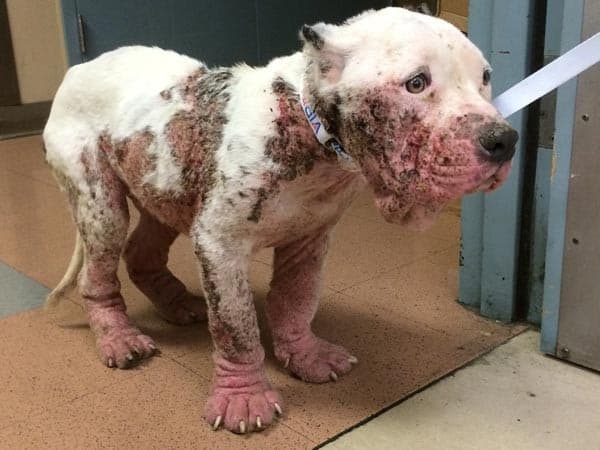
Dog with Demodex Blood Scabies
Signs to identify dogs with scabies
- Itching: This is the most common and recognizable symptom. Dogs usually scratch by their feet, rub against walls or roll on the ground without being biting by an insect (insect stings will have red and itchy stains, but it will go away within a few hours to 1 day).
- Hair Loss: A dog’s coat falls in patches and forms small areas of hair loss, which may be a sign of scabies.
- Flakes: The flakes appear on the hair and skin after the hair falls off, it gradually dry and flake
- Scabies Red Spots: On the dog’s skin, the tiny red spots appear around the area where the hair falls off (carefully pay attention to combine the sign to not mistake for fever-care).
- Skin: The skin thickens, keratinizes, and may bleed from scratching.
- Scabies location: Thin skin areas such as elbows, under the abdomen, behind ears, near the anus, around eyes, nose bridge …
Note the false signs to avoid confusion with other diseases
- Dog’s elbows that are often callused due to lying on a hard floor or being propped up too much can cause thickening of the skin.
- Red spots under the abdomen need to be distinguished from the symptom of care. Dogs with CARE will have a high fever, thick red spots, and diarrhea.
- Red skin is also a sign of fungus, this disease is difficult to distinguish, so you should ask have the veterinarian for help.
How to treat Scabies in Dogs
Scabies is a fairly treatable disease, especially Sarcoptes. Here are a few methods used in folklore:
- Water from pipe tobacco: Soak the water in a clean cotton or brush and apply it to the infected skin. Do 1 time /a day for 3 consecutive days.
- Peppermint Oil: Peppermint oil has antiseptic and cooling properties for the skin. As with water from pipe tobacco, you also apply them to the hair loss area, do 3 times a day, maintain regularity for a month.
- With scabies which is near your dog’s eyes or genitals, you should be careful not to let the oil get into their eyes.
- Peach leaves: Boil peach leaves with water, add salt, and bathe the dog once a day for 3-4 weeks continuously. You can also rub fresh peach leaves directly on the scabies area.
-

Peach Leave for Dog with Scabies Treatment
- Faux Acajen leaves: Like peach leaves, Faux Acajen leaves have antiseptic properties and an acrid taste, boiled it, and bathe the dog. It can help dogs reduce scabies, itching, and hair loss.
- With Demodex scabies, the above remedies are almost less effective. The only way is to get vaccinated from a young age.
- Use special soap to bathe dogs, not use normal soap because its acidity is quite high, causing danger to the dog’s skin.
-
Mitecyn – The Medicine for Dogs with Scabies Read more >>> Important Warning Signs That Your Dog Is Dying and How to Prepare
Preventive measures for dogs with scabies
- Clean and disinfect the place where dogs live.
- Use specialized shower gel to bathe your dog. Note that not bathing frequently will cause dry skin, hair.
- Root galangal: Crush the galangal to get water, apply it on the scabies area.
- Fresh tea leaves, cloves: Boil fresh tea leaves or cloves to bathe dogs.
- Use medicine for external use and injections: For injections, dogs will be more susceptible to liver disease. In addition, dogs may experience neurological concussions, depression, drowsiness, …
- Feed the dog with adequate nutrition to ensure health, increase resistance. In particular, you should stimulate hair growth faster when the dog is sick.
- Vaccinate dogs against diseases when they are young or after adoption if they have not been vaccinated before. Vaccines will reduce the risk of infection with Demodex scabies and this is almost the only method to treat the disease.
Above is all the information on the treatment and prevention of scabies for dogs. We hope it is helpful when you are raising dogs.

